INESC TEC boosts research in health
20 projects in health presented at the Health Cluster Exhibition
INESC TEC took part in the Health Cluster Exhibition in Portugal on 27th September at the Life and Health Sciences Research Institute (ICVS) of the University of Minho in Braga.
The aim of this event was to divulge the technological research taking place in health and promote common ground for R&D institutes, universities, technology transfer offices, hospitals and companies linked to the Portuguese Health cluster. The event also presented the most innovative technology being developed in Portugal in this area.
INESC TEC presented over 20 projects linked to health and wellbeing from almost all of the research units at the institute, as well as the spin-off company Tomorrow Options.


Smart health, a winning proposal
INESC TEC’s mission is to develop internationally competitive R&D and act as an interface between universities, public administration and society. Consequently, the institute aims to increase the quality of the scientific research in Portugal to boost the international competitiveness of Portuguese companies by focusing on socially relevant research with real economic impact.
Smart health is indeed one of the largest challenges. With 20 projects linked to health, INESC TEC is strengthening its position in this area that has great social and economic impact.


Fibre Optic Sensors
Projects Hybrid, Oxygen and SENRONS all apply fibre optics to health. Hybrid is an electro-optical microfluidic device for single cell analysis and diagnosis that is able to diagnose diseases, such as Babesiosis and Malaria. Oxygen uses fibre optics for the distributed measurement of temperature and oxygen dissolved in the blood to make it easier to measure these parameters during magnetic resonance imaging.
SENRONS also uses fibre optic sensors to determine reactive oxygen (ROS) and nitrogen (RNS) species in biological systems. These sensors can be used to measure oxidative species for in vivo studies of oxidative stress using technology based on luminescent nanoparticles capable of discriminating between different reactive species of oxygen and nitrogen.


Optical Imaging and Measurement
FIBDOSE, FLUOROCT and HIRESOMI are INESC TEC projects in the area of optical imaging and measurement that can be applied to clinical diagnosis. FIBDOSE consists of fibre dosimeters for in vitro and in vivo dosimetry in external radiotherapy and brachitherapy. These Dosimetric devices are for real-time quality control in radiotherapy treatment, minimising and optimising the patient’s exposure to ionising radiation. FLUOROCT is based on dose distribution mapping and Monte Carlo simulations for CT-fluoroscopy of radiation transport. The results of this project will help increase patient and staff protection when exposed to radiation. HIRESOMI (HIgh RESolution Optical Measurement and Imaging) uses innovative optical technologies for non-invasive high resolution optical measurements and imaging.


Portable monitoring solutions
INESC TEC is also active in the areas of rehabilitation and physiotherapy through projects PROLIMB and W2M2 and BIOSWIM. PROLIMB uses electronic sensors for the detection and prophylaxis of pathologies of lower limbs by measuring kinematic variables, such as the linear and angular movements of the thigh and legs and also by measuring the myoelectric signals associated with the muscular activity of the most important muscles involved in locomotion. By processing and analysing this information, it can help physicians make decisions regarding therapy. This project aims to obtain a wireless solution to capture these signals that will even work in patients with serious physical impairments or disabilities, as the system will be integrated into a wearable garment of technical fabric.
W2MW (Wireless Wearable Modular Monitoring System) is a simple, low-cost and multifunctional system based on components which can be assembled and managed by physicians, therapists and other healthcare professionals as part of an innovative platform. The project aims to create new models and formulate standards to profoundly alter therapist-patient dynamics. Clinics and hospitals can optimise their ever decreasing resources with this complementary therapy resource. BIOSWIM is a Body interface system based on integration monitoring that can be worn by the patient. It is a universal solution to monitor physiological and biomechanical signals from a swimmer under normal training conditions, both in and out of the water with possible applications in hydrotherapy.
Electronic and Optoelectronic System Integration
SMARTBIO, BIOMOTION and BIOPELVIC also focus on physical rehabilitation and medical prosthesis. SMARTBIO looks at hip femoral prosthesis for in vivo loosening data acquisition. Total hip arthroplasty joins the prosthetic hip to the bone with biocompatible material with high success rates. SMARTBIO is a feasibility study of a laboratorial system to identify the beginning of fractures in the bone cement mantle that can appear as the bone cement decomposes and the joint is used over time. It is a non-invasive monitoring method of hip prosthesis loosening with embedded optical Bragg fibre sensors with wireless communication systems to define clinical prevention and correction methodologies.
BIOMOTION focuses on a perception of biological locomotion, integrated psychophysics, neurophysiology and computational modelling. This project will help understand the functional aspects of vision, it will extract data relevant to artificial vision and evaluate the possibility of manufacturing optical structures of this type.
BIOPELVIC is a study of female pelvic floor disorders. Vaginal prolapse, urinary and bowel incontinence and other abnormalities related to the urinary and gastrointestinal systems are all connected to the pelvic floor muscles and they affect 40% of the world population between the ages of 45 and 85. Using ultrasound, image processing and 3D reconstruction, an anatomic model with the cinematic dynamics and characteristics of the pelvic cavity will help doctors make decisions regarding diagnosis and trauma treatment for patients and their families.
Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition
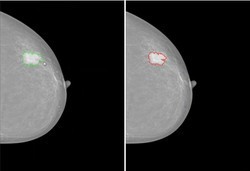
Projects BCCT, Semantic PACS focus on the aesthetic results of mastectomies and breast cancer diagnosis. BCCT.core (Breast Cancer Conservative Treatment) is a computer-aided medical system to objectively and automatically aesthetically evaluate the results of BCCT and improve practices.
SEMANTIC PACS is an innovative system with 100% reliability in the detection of malignant tumours. The system reduces waiting times for diagnosis and therefore patient distress. The project represents a significant step forward in the detection of breast cancer.
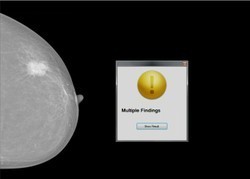
INESC TEC has another project in breast cancer diagnosis - MammoClass. This tool is able to estimate the level of malignancy of lumps found in mammograms based on BIRADS (Breast Imaging and Report Data System). The tool is available online and can be used by doctors and radiologists to aid in diagnosis.
Computer Graphics and Virtual Environments for Ambient Assisted Living
Projects CAALYX, eCAALYX, CAALYX-MV, AAL4ALL, ICT4Depression and LUL are all developing new technology for Ambient Assisted Living, supporting senior citizens and people with special needs. CAALYX - Complete Ambient Assisted Living Experiment is a system that offers senior citizens a higher level of autonomy with clear, non-intrusive remote monitoring systems that allow them to remain living in their own home for longer.
eCAALYX is part of the AAL Joint European Programme that aims to develop a roaming monitoring system for users with several chronic illnesses (comorbidity). Project CAALYX-MV promotes the technology developed in the CAALYX projects. The aim is to increase senior citizens’ independence at home and delay hospitalisation or being admitted to nursing homes for longer. The CAALYX system aims to monitor the health and wellbeing of its users and provide them with tools and services that focus on their comfort, security, energy efficiency and communications, to support their daily activities.
Project AAL4ALL promotes an industrial “ecosystem” to increase the products and services available for Ambient Assisted Living (ALL) in Portugal. The project focuses on defining specific patterns to develop products and services that make it possible to reduce costs and improve the quality of life of Portuguese senior citizens.
LUL (Living Usability Lab) is a project on Next Generation Networks that provides innovative services and technologies to improve the quality of life of senior citizens and people with special needs, promoting active ageing.
The final project in this area is ICT4Depression. This project aims to help individuals that suffer from depression by using a system that continually monitors a person’s need and activities. This project is different to existing systems because it uses non intrusive biosensors that are linked to the patient’s body. These sensors provide data on heart rates and information on other vital signs. This information is then sent to patient’s mobile phones using Bluetooth or the internet along with suggestions for actions to respond to the patient’s needs.

Information Management and Systems in the Fight Against HIV/AIDS
SI.VIDA is INESC TEC’s project that aims to develop a vertical information system for the National Health Services for HIV/AIDS – Ministry of Health (CNSIDA). It will be distributed and used by health centres that treat people with HIV/AIDS. In addition to standardising clinical processes, the IT system for HIV/AIDS (SI.VIDA) should make data transfer more transparent and improve the evaluation and management of the human resources involved. This system is already being used or tested in several hospitals: the São João Hospital (Porto), the Egas Moniz Hospital (Lisbon), the Hospital of Faro, the Hospital of Vila Nova Gaia and the University Hospital in Coimbra.
Optimisation and Decision Support
KEP (New models for enhancing the kidney transplantation process) is an INESC TEC project that aims to research and develop new methods to facilitate and improve the decisions made on kidney transplants with live donors. KEP is an important public health planning and management project as it develops advanced optimising methods to resolve situations when patients have incompatible live donors. The idea of donor-patient pair exchanges is known as Paired Kidney Exchange, PKE, and means that each patient receives a kidney from the donor of the other pair. In order to obtain the highest number of PKEs, a solution has to be developed to maximise the number of transplants in accordance with patient compatibility.
WalkinSense, developed by Tomorrow Options, an INESC Porto spin-off, is another project that must be highlighted. Every year, 15% of diabetes sufferers in the UK will develop a foot ulcer and for 15% of them, amputation is the only option. WalkinSense is a gait analysis medical device that provides quantitative and qualitative information regarding users' dynamic plantar pressure and activity. Targeted at clinical activities, it provides information for the prescription or assessment of orthoses and the comparison of patients' tests to assess evolution. WalkinSense can be used within a clinical environment, such as in: orthopaedics, neurology, cardiology, podiatry, rehabilitation and sports applications.

Optimisation, Data Mining and Simulation
Finally, project ORPlan (An integrated framework for operating room capacity planning and scheduling) must be highlighted. The project aims to develop an integrated framework for operating theatre capacity planning and scheduling and builds a framework to tackle the problem of operating theatre optimisation with a combination of advanced data mining, optimisation and simulation techniques. A software prototype was implemented to manually plan surgery scheduling and the R&D team is now working on optimisation modules that will be integrated into the framework.
These projects reveal the fact that INESC TEC’s involvement in the development of applications for health has grown, highlighting the importance of investing in these technologies to improve the quality of life for patients, senior citizens, the chronically ill and individuals with reduced mobility.